该模块提供了实数数学函数的访问接口。除非另有明确说明,否则所有返回值均为浮点数。
数论与表示函数
ceil(x)
返回x的向上取整值,即大于或等于x的最小的整数。如果x普通对象,则委托给x.__ceil__方法 ,它应该返回一个Integral类型值。
>>>from math import ceil
>>>ceil(1.23)
2
>>>ceil(-1.23)
-1
>>>ceil(5)
5
>>>ceil(-5)
-5
>>>from fractions import Fraction
>>>ceil(Fraction(5,4))
2
>>>ceil(-Fraction(5,4))
-1
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
class CeilTest: def __init__(self,num=0): self.num=num def __ceil__(self): if self.num!=0: return 1 else: return 0
>>>ceil(CeilTest(0.01))
1
>>>ceil(CeilTest(-0.01))
1
>>>ceil(CeilTest(-0.0))
0
comb(n, m)
返回不重复且无顺序地从n项中选择m项的方案数(整数),即组合公式。
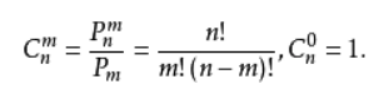
当 m <= n 时取值为 n! / (m! * (n - m)!);当 m > n 时取值为零。n!表示从1连乘到n(阶乘)。
也称为二项式系数,因为它等价于二项式 (1 + x) ** n展开中第m项的系数。
如果任一参数不为整数则会抛出TypeError异常。如果任一参数为负数则会抛出ValueError异常。
·
·
·
·
·
def Pmn(n,m): rst=n for i in range(n-1,n-m,-1): rst*=i return rst
>>>from math import comb
>>>comb(7,5),Pmn(7,5)//Pmn(5,5)
(21,21)
>>>comb(7.0,5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
>>>comb(7,5.)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'float' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
>>>comb(7,0)
1
>>>comb(-7,5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: n must be a non-negative integer
>>>comb(7,-5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: k must be a non-negative integer
copysign(x, y)
返回一个浮点数,绝对值等于x的绝对值,与y的符号相同。在支持带符号零(-0.0)的平台上,copysign(1.0, -0.0) 返回 -1.0。
>>>from math import copysign
>>>copysign(-1.23, -0.1),-abs(-1.23) if -0.1<0 else abs(-1.23)
(-1.23, -1.23)
>>>copysign(1.0,0.0),copysign(1.0,-0.0)
(1.0, -1.0)
fabs(x)
返回 x 的绝对值。
>>>from math import fabs
>>>fabs(-1.23),abs(-1.23)
(-1.23, -1.23)
factorial(x)
返回整数 x 的阶乘。如果 x 为分数,则将抛出 TypeError。如果 x 为负整数,则将抛出 ValueError。3.9版后如果x为带整数部分的正浮点数,则(首次调用打出DeprecationWarning)如果小数部分为0返回计算值,否则抛出ValueError异常。
>>>from math import factorial
>>>factorial(5),1*2*3*4*5
(120, 120)
>>>from fractions import Fraction
>>>factorial(Fraction(10,1))
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'Fraction' object cannot be interpreted as an integer
>>>factorial(-5)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: factorial() not defined for negative values
>>>factorial(5.0)
<stdin>:1: DeprecationWarning: Using factorial() with floats is deprecated
120
>>>factorial(5.0)
120
>>>factorial(5.9)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: factorial() only accepts integral values
floor(x)
返回x的向下取整,即小于或等于x的最大整数。如果x是普通对象,则委托给x.__floor__方法 ,它应该返回一个Integral类型值。
>>>from math import floor
>>>floor(1.99),floor(-1.01)
(1, -2)
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
·
class FloorTest1: def __init__(self,num=0): self.num=num def __floor__(self): if self.num!=0: return 1 else: return 0class FloorTest2: def __init__(self,num=0): self.num=num def __floor__(self): if self.num!=0: return 1. else: return 0.
>>>floor(FloorTest1(1.99)),floor(FloorTest2(-.0))
(1, 0.0)
fmod(x, y)
返回x除以y的余数,即对于某个整数n,使返回结果x-n*y与x有相同的符号,绝对值小于y的绝对值。功能上与x%y非常相似,但有以下两点不同:
1、如果x和y都是整数,x%y的结果是整数,而fmod(x,y)是浮点数;
>>>from math import fmod
>>>fmod(7,5),7%5
(2.0, 2)
2、由于fmod对浮点运算进行了优化,所以可以保证“结果x-n*y与x有相同的符号,绝对值小于y的绝对值”,但对于某些浮点数,表达式 x % y出现与y符号相同和绝对值不小于y的绝对值的情况。
>>>fmod(-1e-100, 1e100), -1e-100 % 1e100
(-1e-100, 1e+100)
因此对于整数求余数,首选x%y;对于浮点数首选fmod。
frexp(x)
以 元组(m, e) 对的形式返回 x 的尾数和指数。m 是一个浮点数, e 是一个整数,正好是 x == m * 2**e 。如果 x 为零,则返回 (0.0, 0) ,否则返回元组 (m, e),其中 0.5 <= abs(m) < 1 。这种“分离”浮点数的表示方法,很少在程序中使用,一般用于不同系统间数据交换。
>>>from math import frexp
>>>frexp(0)
(0.0, 0)
>>>frexp(0.1)
(0.8, -3)
fsum(iterable)
通过优化浮点计算来避免精度损失,返回序列或集合中的精确浮点统计值。
>>>from math import fsum
>>>sum([.1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1])
0.9999999999999999
>>>fsum([.1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1, .1])
1.0
gcd(*integers)
返回给定的整数参数的最大公约数。如果有一个参数非零,则返回值将是能同时整除所有参数的最大正整数。如果所有参数为零或不带参数返回 0。
>>>from math import gcd
>>>gcd(),gcd(0,0,0),gcd(12,8,0,36),gcd(12,8,18,36)
(0, 0, 4, 2)
isclose(a, b, *, rel_tol=1e-09, abs_tol=0.0)
若 a 和 b 的值比较接近则返回 True,否则返回 False。
根据给定的绝对和相对容差确定两个值是否接近。
rel_tol 是相对容差 —— a和b之差的绝对值与a和b绝对值中最大者之比的最大允许值。 例如,要设置5%的容差,请传入rel_tol=0.05 。相对容差默认值为1e-09,确保两个值在大约9位十进制数字内相同,必须为非负数。
>>>from math import isclose
>>>isclose(3.1415,3.1416)
False
>>>isclose(3.1415,3.1416,rel_tol=0.0005)
True
>>>isclose(3.1415926535897,3.1415926535898)
True
>>>isclose(3.1415926535897,3.1415926535898,rel_tol=0.0)
False
>>>isclose(3.1416,3.1416,rel_tol=-0.000000001)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: tolerances must be non-negative
abs_tol是绝对容差 —— a和b之差的绝对值如果小于该值就认为是接近的。把相对容差置0(rel_tol=0.0),绝对容差是某个特定的数,这个函数就可以用来判断浮点数是否相等。如果a和b中有一个数是0.0,那么就可用来判断另一个浮点数是否是0.0。这对于接近零的数的比较很有用。abs_tol默认值是0.0,必须为非负数。
>>>isclose(3.1415,3.1416,rel_tol=0.0)
False
>>>isclose(3.1415,3.1416,rel_tol=0.0,abs_tol=0.0001)
True
>>>isclose(1e-20,0.0,rel_tol=0.0)
False
>>>isclose(1e-20,0.0,rel_tol=0.0,abs_tol=9.8e-20)
True
>>>isclose(3.1415,3.1416,rel_tol=0.0,abs_tol=-0.0001)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: tolerances must be non-negative
如果相对容差和绝对容差都不为0.0,采用以下的逻辑判断结果(a和b之差的绝对值不大于相对容差所转的绝对容差和输入的绝对容差两者中的最大值。):
abs(a-b) <= max(rel_tol * max(abs(a), abs(b)), abs_tol) 。
>>>isclose(3.1415,3.1416,rel_tol=0.00005,abs_tol=0.00001)
True
>>>abs(3.1415-3.1416),0.00005*max(3.1415,3.1416),0.00001
(9.999999999976694e-05, 0.00015708, 1e-05)
>>>abs(3.1415-3.1416)<=max(0.00005*max(3.1415,3.1416),0.00001)
True
另外,NaN不接近任何值(包括 NaN),inf和-inf只接近自己。
>>>from math import nan,inf
>>>isclose(nan,0.0)
False
>>>isclose(nan,nan)
False
>>>isclose(inf,-inf)
False
>>>isclose(inf,inf)
True
>>>isclose(-inf,-inf)
True